NASA’s ambitious mission is to use space-based observatories to map the sky in 3D, with a target launch date of late February 2025.
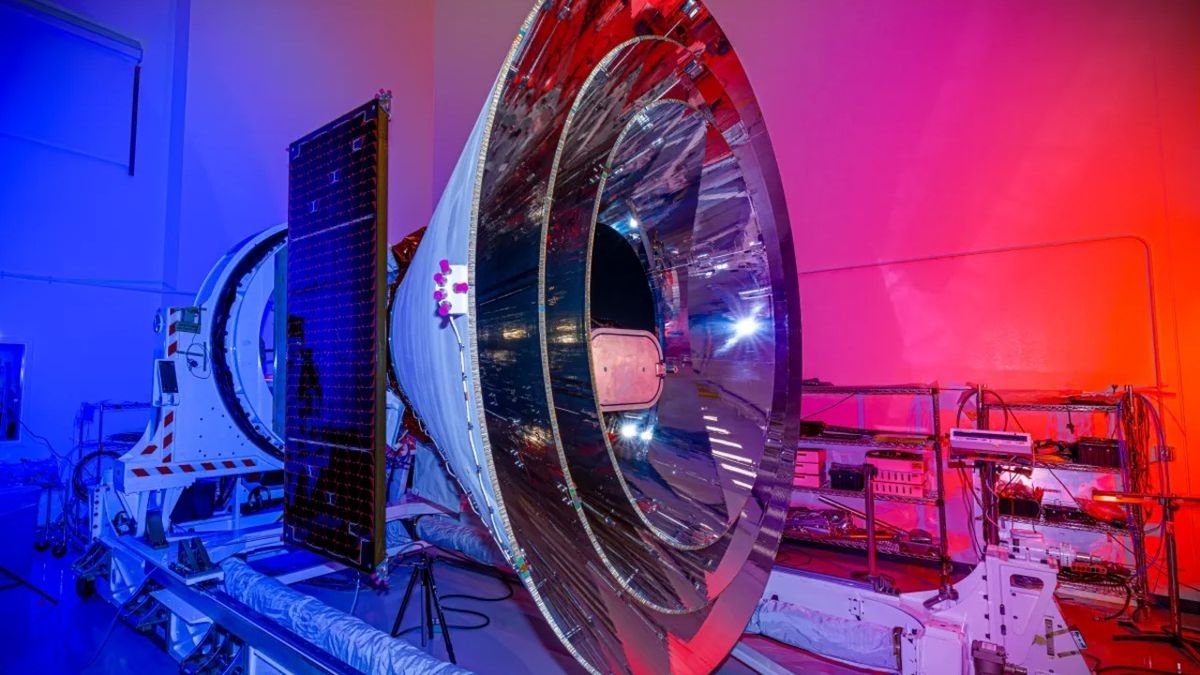
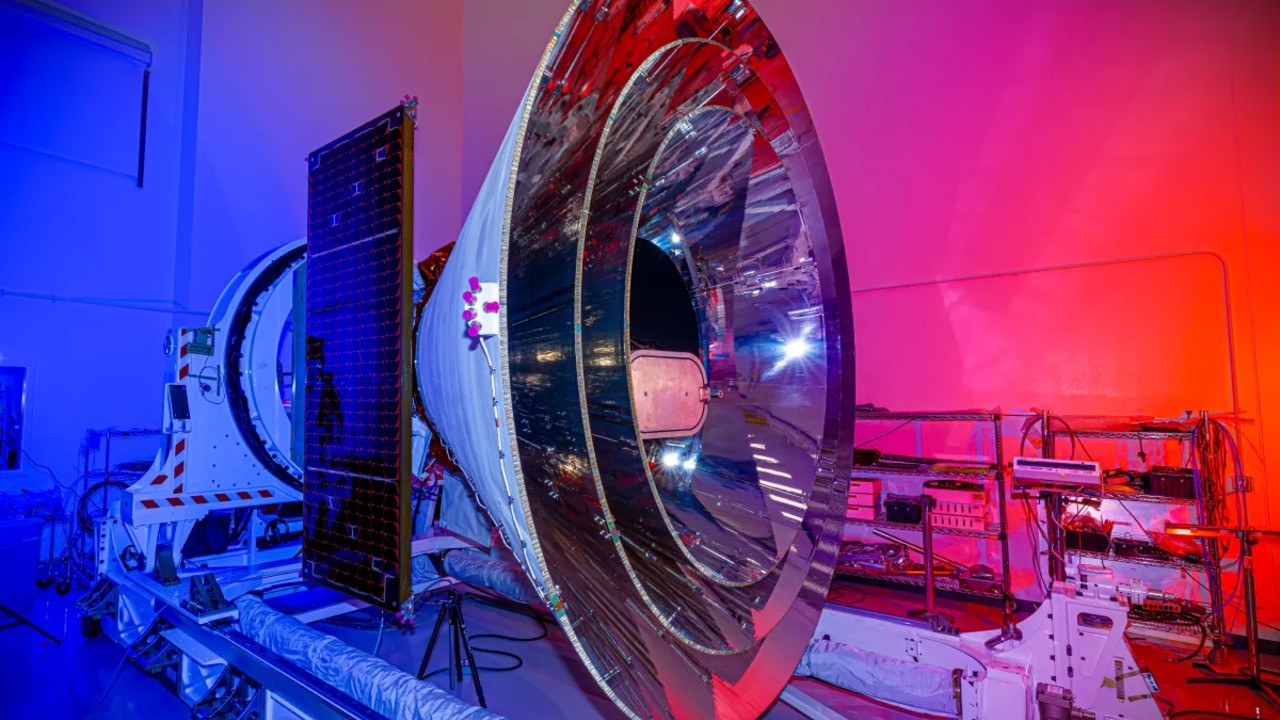
NASA’s compact car-sized observatory called the Cosmic History Spectrophotometer, Epoch of Reionization and Ice Explorer (or simply the Spectrophotometer) SPHEREx abbreviation), millions of maps will be drawn Star Galaxies can be seen from all directions around our planet, “like scanning the interior of the Earth,” according to one agency statement. The satellite will be launched to Space Exploration Technologies Corporation A Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
Using sky maps, SPHEREx needs to achieve three scientific goals. First, by measuring the distribution of hundreds of millions of galaxyNASA is trying to learn more about an ancient cosmic event called inflation, in which the universe grew exponentially within a fraction of a second after it occurred. big Bang. If the observatory succeeds, scientists may learn more about the physics behind inflation and what drives the phenomenon.
Second, NASA is looking for a more complete picture of the objects and sources that radiate throughout the known region. universe. The observatory will collect data that will allow scientists to measure the “collective luminescence” of distant galaxies, including those from hidden galaxy Never observed alone before.
Finally, the SPHEREx mission will search our own galaxy, Milky Waythe ingredients needed for life, including carbon dioxide and water. If SPHEREx finds them, it could give scientists clues about how likely these ingredients are to be present when new planets form.
Scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) developed and built SPHEREx, which has a planned life of two years. During this time, SPHEREx should Two maps are produced each yearAccording to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
SpaceX wins launch contract Back to 2021. The 329-pound (178-kilogram) spacecraft will carry Falcon 9 rocket The launch location is Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. JPL leads the entire mission, including operations, systems engineering, integration and testing.
The second payload of the same Falcon 9 launch was a constellation of four small satellites representing NASA punch mission (Politometer to unify corona and heliosphere). These satellites are heading to low Earth orbit. They will observe the sun’s outer layers crownstudies how mass and energy are converted into the solar wind.