- Trillium is generally available just months after its preview release
- Powerful AI chip provides more than four times training performance
- Google uses it to train the company’s advanced artificial intelligence model Gemini 2.0
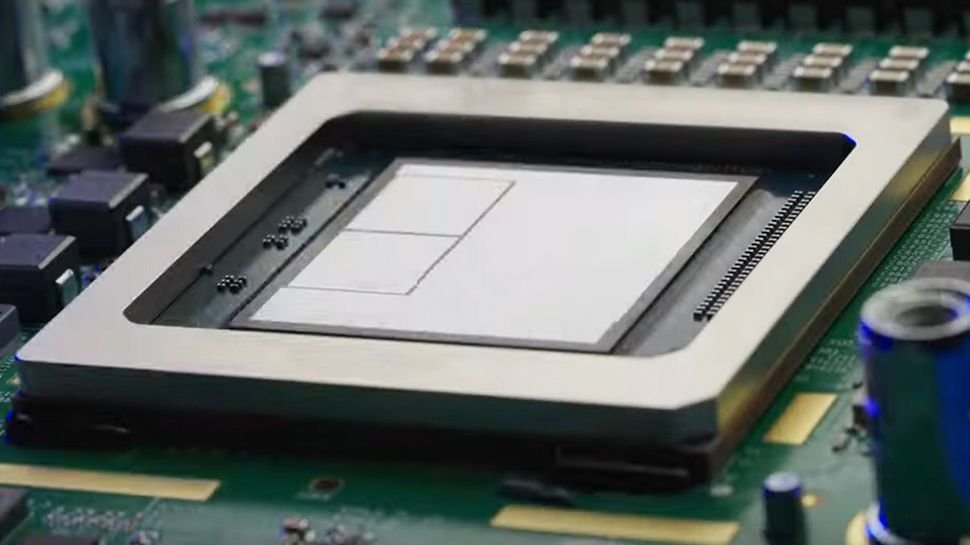
Google The company has been developing tensor processing units (TPUs), its custom artificial intelligence accelerator, for more than a decade and a few months later Available in previewannounced that its sixth-generation TPU is generally available and now available for rent.
Trillium doubled the HBM capacity and chip-to-die interconnect bandwidth and used it to train Gemini 2.0, the tech giant’s flagship artificial intelligence model.
Google reports a 2.5x improvement in training performance per dollar compared to previous generations of TPUs, making it an attractive option for enterprises looking for efficient AI infrastructure.
Google Cloud’s AI supercomputer
Trillium offers a host of other improvements over its predecessor, including four times more training performance. Energy efficiency is improved by 67%, while peak computing performance per die is increased by 4.7 times.
Trillium naturally improves reasoning performance as well. Google’s tests show that compared to previous generations of TPUs, the throughput of image generation models such as Stable Diffusion XL has increased by more than three times, and the throughput of large language models has increased by nearly twice.
The chip is also optimized for embedding-intensive models, with its third-generation SparseCore providing better performance for dynamic and data-dependent operations.
Trillium TPU also forms the basis of Google Cloud’s artificial intelligence supercomputer. The system has more than 100,000 Trillium chips connected through the Jupiter network structure, providing a bandwidth of 13 Petabits/sec. It integrates optimized hardware, open software and popular machine learning frameworks, including JAX, PyTorch and TensorFlow.
With Trillium now generally available, Google Cloud customers have access to the same hardware used to train Gemini 2.0, making high-performance AI infrastructure more accessible for a variety of applications.